Statistics for Timemania
Statistics of real draws
Timemania statistics only consider draws carried out since May 7, 2022, when the rules/matrix changed (participating teams were changed).
Timemania (until the draw 2217 on
Mar 13, 2025)
Distribution in quadrants
Distribution of drawn numbers in each quadrant
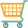
Quadrant 4
46-50, 56-60, 66-70, 76-80
Quantity drawn in the quadrant
Actual frequency
Expected frequency
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
Quantity
drawn in the quadrant
|
Actual
occurrences
|
Expected
occurrences
|
Last
draw
|
Shortest
interval
|
Longest
interval
|
Current
interval
|
Average
interval
|
|
0
|
286
|
269
|
2216
|
1
|
38
|
1
|
7.75
|
|
1
|
692
|
698
|
2215
|
1
|
24
|
2
|
3.20
|
|
2
|
704
|
724
|
2217
|
1
|
23
|
0
|
3.15
|
|
3
|
403
|
387
|
2213
|
1
|
31
|
4
|
5.49
|
|
4
|
108
|
115
|
2196
|
1
|
139
|
21
|
20.33
|
|
5
|
22
|
19
|
2112
|
2
|
309
|
105
|
96.00
|
|
6
|
2
|
1
|
1845
|
144
|
1701
|
372
|
922.50
|
|
7
|
0
|
0
|
|
|
|
2217
|
0.00
|
- The table shows data on the quantity of drawn numbers in each quadrant, considering all draws of timemania (with the current matrix).
- Actual occurrences are the real total occurrences of a quantity of numbers in the referred quadrant.
- Expected occurrences are the expected occurrences of each quantity of numbers in the referred quadrant, according to mathematical probability.
- Last draw is the most recent draw in which that quantity of numbers was drawn in the referred quadrant.
- Shortest interval is the shortest gap between draws in which that quantity of numbers was drawn in the referred quadrant.
- Longest interval is the longest gap between draws in which that quantity of numbers was drawn in the referred quadrant.
- Current interval is the current interval since the last draw in which that quantity of numbers was drawn in the referred quadrant.
- Average interval is the general average of intervals between draws in which that quantity of numbers was drawn in the referred quadrant (until the last draw in which that quantity of numbers was drawn in the referred quadrant).
- The actual and expected occurrences tend to get closer to each other the largest the sample.
Main
Results
Statistics
Wheels
Subscription